EDB: SIwave DC-IR Analysis#
This example demonstrates the use of EDB to interact with a PCB layout and run DC-IR analysis in SIwave. Perform required imports
[1]:
import os
import tempfile
import time
import pyedb
from pyedb.misc.downloads import download_file
temp_dir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory(suffix=".ansys")
targetfile = download_file("edb/ANSYS-HSD_V1.aedb", destination=temp_dir.name)
siwave_file = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(targetfile), "ANSYS-HSD_V1.siw")
print(targetfile)
aedt_file = targetfile[:-4] + "aedt"
C:\Users\ansys\AppData\Local\Temp\tmpw3o5n1ge.ansys\edb/ANSYS-HSD_V1.aedb
Launch Ansys Electronics Database (EDB)#
Instantiate an instance of the pyedb.Edb class using SI units.
[2]:
if os.path.exists(aedt_file):
os.remove(aedt_file)
# Select EDB version (change it manually if needed, e.g. "2024.2")
edb_version = "2024.2"
print(f"EDB version: {edb_version}")
edb = pyedb.Edb(edbpath=targetfile, edbversion=edb_version)
EDB version: 2024.2
PyEDB INFO: StdOut is enabled
PyEDB INFO: Logger is initialized in EDB.
PyEDB INFO: legacy v0.35.dev0
PyEDB INFO: Python version 3.10.11 (tags/v3.10.11:7d4cc5a, Apr 5 2023, 00:38:17) [MSC v.1929 64 bit (AMD64)]
PyEDB INFO: Database ANSYS-HSD_V1.aedb Opened in 2024.2
PyEDB INFO: Cell main Opened
PyEDB INFO: Builder was initialized.
PyEDB INFO: EDB initialized.
Identify nets and components#
The Edb.nets.netlist and Edb.components.instances properties contain information about all of the nets and components. The following cell uses this information to print the number of nets and components.
[3]:
print("Nets {}".format(len(edb.nets.netlist)))
start = time.time()
print("Components {}".format(len(edb.components.instances.keys())))
print("elapsed time = ", time.time() - start)
Nets 348
Components 509
elapsed time = 0.0
Identify pin positions#
This code shows how to obtain all pins for a specific component and print the [x, y] position of each pin.
[4]:
pins = edb.components["U2"].pins
count = 0
for pin in edb.components["U2"].pins.values():
if count < 10: # Only print the first 10 pin coordinates.
print(pin.position)
elif count == 10:
print("...and many more.")
else:
pass
count += 1
[0.13149999608000001, 0.018999997560000016]
[0.13099999708, 0.018999997560000016]
[0.13049999808, 0.018999997560000013]
[0.12999999654000002, 0.01899999756000001]
[0.12949999754000002, 0.01899999756000001]
[0.12899999854000002, 0.01899999756000001]
[0.12849999700000003, 0.018999997560000006]
[0.12799999800000003, 0.018999997560000002]
[0.12749999646000001, 0.018999997560000002]
[0.12699999746, 0.018999997560000002]
...and many more.
Get all nets connected to a specific component. Print the pin and the name of the net that it is connected to.
[5]:
connections = edb.components.get_component_net_connection_info("U2")
n_print = 0 # Counter to limit the number of printed lines.
print_max = 15
for m in range(len(connections["pin_name"])):
ref_des = connections["refdes"][m]
pin_name = connections["pin_name"][m]
net_name = connections["net_name"][m]
if net_name != "" and (n_print < print_max):
print('{}, pin {} -> net "{}"'.format(ref_des, pin_name, net_name))
n_print += 1
elif n_print == print_max:
print("...and many more.")
n_print += 1
U2, pin 20 -> net "1V0"
U2, pin 21 -> net "1V0"
U2, pin 22 -> net "1V0"
U2, pin 23 -> net "1V0"
U2, pin 24 -> net "1V0"
U2, pin 25 -> net "1V0"
U2, pin 26 -> net "1V0"
U2, pin 27 -> net "1V0"
U2, pin 28 -> net "1V0"
U2, pin 32 -> net "GND"
U2, pin 33 -> net "GND"
U2, pin 34 -> net "GND"
U2, pin 35 -> net "GND"
U2, pin 36 -> net "GND"
U2, pin 37 -> net "GND"
...and many more.
Compute rats.
[6]:
rats = edb.components.get_rats()
Identify connected nets#
The get_dcconnected_net_list() method retrieves a list of all DC-connected power nets. Each group of connected nets is returned as a set. The first argument to the method is the list of ground nets, which are not considered in the search for connected nets.
[7]:
GROUND_NETS = ["GND", "GND_DP"]
dc_connected_net_list = edb.nets.get_dcconnected_net_list(GROUND_NETS)
for pnets in dc_connected_net_list:
print(pnets)
{'NetD3_2', 'AVCC_1V3'}
{'2V5', '1.8V_DVDDH', 'NetC271_1'}
{'1.2V_AVDDL', '1.2V_DVDDL', '1.2V_AVDLL_PLL'}
{'SFPA_VCCR', 'NetIC1_8', 'USB3_VBUS', 'PDEN', '5V', 'SFPA_VCCT', '3.3V_AVDDH'}
{'VDD_DDR', 'NetR22_1'}
{'1V0', 'NetR8_1'}
Power Tree#
The power tree provides connectivity through all components from the VRM to the device.
[8]:
VRM = "U1"
OUTPUT_NET = "AVCC_1V3"
powertree_df, component_list_columns, net_group = edb.nets.get_powertree(OUTPUT_NET, GROUND_NETS)
Print some information about the power tree.
[9]:
print_columns = ["refdes", "pin_name", "component_partname"]
ncol = [component_list_columns.index(c) for c in print_columns]
This prints the header. Replace “pin_name” with “pin” to make the header align with the values.
[10]:
print("\t".join(print_columns).replace("pin_name", "pin"))
for el in powertree_df:
s = ""
count = 0
for e in el:
if count in ncol:
s += "{}\t".format(e)
count += 1
s.rstrip()
print(s)
refdes pin component_partname
L10 1 WE-Coil-PD4-S
IC2 1 SOIC127P-680x175-8_N
D3 2 DO214AA
R1 1 RESC1608X05N
L10 2 WE-Coil-PD4-S
C46 1 CAPMP7343X31N
C53 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C68 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C52 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C45 1 CAPC1608X08N
C55 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C58 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C54 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C60 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C57 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C73 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C69 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C56 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C205 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C238 2 CAPC1005X33X10LL5
C145 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C144 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C143 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C142 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C141 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C140 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C139 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C138 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C137 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C136 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C135 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C134 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C133 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C132 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C131 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C130 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C129 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
C128 2 CAPC0603X33X15LL03T05
U1 D28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 D29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 F28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 F29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 H28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 H29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 K28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 K29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 M15 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 M28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 M29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 P13 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 P22 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 P24 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 P28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 P29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 T10 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 T28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 T29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 V28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 V29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 W11 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 W18 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 W19 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 Y11 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 Y28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 Y29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AB28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AB29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AD11 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AD28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AD29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AE23 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AF13 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AF23 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AF28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AF29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AG19 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AH16 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AH28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AH29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AK28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AK29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AM28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AM29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AP28 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
U1 AP29 ALTR-FBGA1517-Ansys
Remove unused components#
Delete all RLC components that are connected with only one pin. The Edb.components.delete_single_pin_rlc() method provides a useful way to remove components that are not needed for the simulation.
[11]:
edb.components.delete_single_pin_rlc()
PyEDB INFO: Deleted 0 components
[11]:
[]
You can also remove unused components explicitly by name.
[12]:
edb.components.delete("C380")
[12]:
True
Nets can also be removed explicitly.
[13]:
edb.nets.delete("PDEN")
[13]:
['PDEN']
Print the top and bottom elevation of the stackup obtained using the Edb.stackup.limits() method.
[14]:
s = 'Top layer name: "{top}", Elevation: {top_el:.2f} '
s += 'mm\nBottom layer name: "{bot}", Elevation: {bot_el:2f} mm'
top, top_el, bot, bot_el = edb.stackup.limits()
print(s.format(top=top, top_el=top_el * 1e3, bot=bot, bot_el=bot_el * 1e3))
Top layer name: "1_Top", Elevation: 1.75 mm
Bottom layer name: "16_Bottom", Elevation: 0.000000 mm
Set up for SIwave DCIR analysis#
Create a voltage source and then set up a DCIR analysis.
[15]:
edb.siwave.create_voltage_source_on_net("U1", "AVCC_1V3", "U1", "GND", 1.3, 0, "V1")
edb.siwave.create_current_source_on_net("IC2", "NetD3_2", "IC2", "GND", 1.0, 0, "I1")
setup = edb.siwave.add_siwave_dc_analysis("myDCIR_4")
setup.use_dc_custom_settings = True
setup.set_dc_slider = 0
setup.add_source_terminal_to_ground("V1", 1)
[15]:
True
Solve#
Save the modifications and run the analysis in SIwave.
[16]:
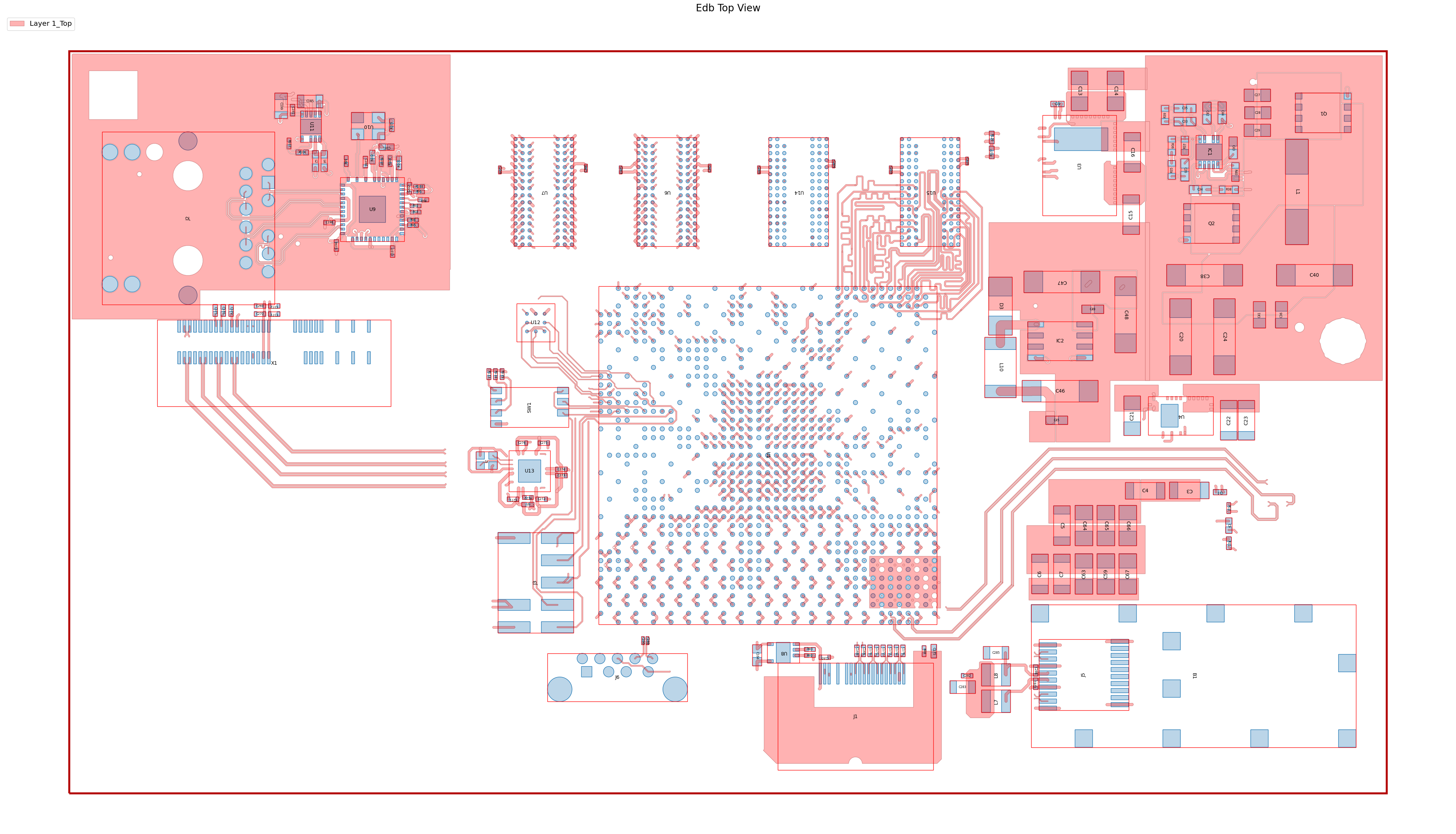
edb.save_edb()
edb.nets.plot(None, "1_Top", plot_components_on_top=True)
PyEDB INFO: EDB file save time: 0.00ms
PyEDB INFO: Plot Generation time 10.799
[16]:
(<Figure size 6000x3000 with 1 Axes>, <Axes: title={'center': 'Edb Top View'}>)
[17]:
siw_file = edb.solve_siwave()
Export results#
Export all quantities calculated from the DC-IR analysis. The following method runs SIwave in batch mode from the command line. Results are written to the edb folder.
[18]:
outputs = edb.export_siwave_dc_results(
siw_file,
setup.name,
)
['"C:\\Program Files\\AnsysEM\\v242\\Win64\\siwave.exe"', '-embedding', '-RunScriptAndExit', '"C:\\Users\\ansys\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\tmpw3o5n1ge.ansys\\edb\\export_results.py"']
Close EDB. After EDB is closed, it can be opened by AEDT.
[19]:
edb.close_edb()
PyEDB INFO: EDB file release time: 0.00ms
[19]:
True
View Layout in SIwave#
The SIwave user interface can be visualized and manipulated using the SIwave user interface. This command works on Window OS only.
[20]:
# siwave = pyedb.Siwave("2024.2")
# siwave.open_project(siwave_file)
# report_file = os.path.join(temp_folder,'Ansys.htm')
# siwave.export_siwave_report("myDCIR_4", report_file)
# siwave.close_project()
# siwave.quit_application()
Clean up the temporary files and directory.
[21]:
temp_dir.cleanup()
